Myocardial Infarction (MI) ya Heart Attack ek serious medical emergency hai jisme heart ke muscles (myocardium) ko blood supply achanak band ho jati hai.
Iske wajah se heart ke tissue me oxygen nahi pahuch pati aur wo damage ya dead ho jata hai.
Agar time pe treatment na mile to patient ki jaan bhi ja sakti hai.
📘 Definition
Myocardial Infarction is defined as:
“Death of heart muscle tissue due to sudden interruption of blood supply through the coronary arteries.”
Simple words me:
Jab heart ke kisi part tak blood nahi pahuchta, to wo part mar jaata hai — ise hi myocardial infarction kehte hain.
❤️ Anatomy Reminder (Short)
Heart ek muscular organ hai jise blood supply coronary arteries deti hain.
- Left coronary artery (LCA) → supplies left side of heart
- Right coronary artery (RCA) → supplies right side
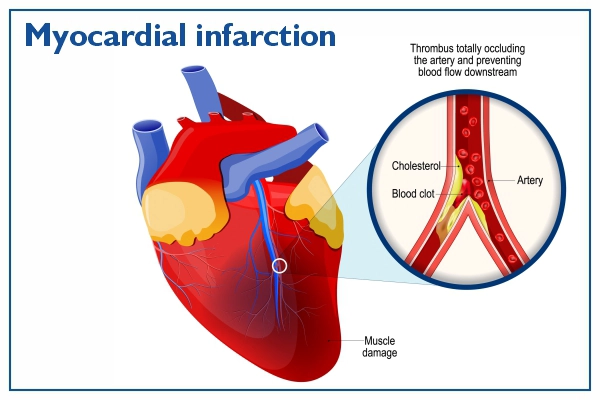
Agar in arteries me blockage (clot, fat deposit, plaque) ho jaye, to oxygen supply band ho jati hai — aur heart attack hota hai.
⚠️ Causes / Risk Factors
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle | Smoking, Alcohol, Lack of exercise |
| Medical Conditions | Hypertension, Diabetes, High cholesterol |
| Dietary | High-fat, oily foods |
| Psychological | Stress, Anxiety |
| Other | Obesity, Family history of heart disease, Old age |
🧠 Pathophysiology (Simple Explanation)
1️⃣ Coronary artery me fatty plaque jamti hai (Atherosclerosis).
2️⃣ Plaque rupture hone par blood clot (thrombus) banta hai.
3️⃣ Clot artery ko block kar deta hai.
4️⃣ Blood aur oxygen supply band ho jati hai.
5️⃣ Affected heart muscle necrotic (dead) ho jata hai.
6️⃣ Isse pain, arrhythmia, heart failure ya even death ho sakti hai.
💉 Signs and Symptoms
- Sudden, severe chest pain (pressure type, radiating to left arm, neck, or jaw)
- Sweating (cold and clammy skin)
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Anxiety or restlessness
- Paleness of face
- Weak pulse and low blood pressure
- Sometimes silent MI (especially in diabetic patients)
🧬 Diagnosis
| Test Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ECG (Electrocardiogram) | ST elevation or T wave inversion shows MI |
| Troponin Test | Detects cardiac muscle damage |
| CK-MB Test | Measures cardiac enzyme level |
| Echocardiography | Checks motion of heart wall |
| Coronary Angiography | Identifies site of blockage |
🏥 Treatment and Management
1️⃣ Emergency Management
- Keep patient calm and in semi-Fowler’s position
- Give Oxygen therapy
- Administer Aspirin (to prevent further clotting)
- Give Nitroglycerin (GTN) under the tongue for chest pain
- Morphine may be given for severe pain (under doctor supervision)
- Shift immediately to ICU or cardiac care unit
2️⃣ Medical Treatment
- Thrombolytic drugs – dissolve blood clot (e.g. Streptokinase, Alteplase)
- Anticoagulants – prevent further clotting (Heparin, Warfarin)
- Beta blockers – reduce heart workload (Metoprolol)
- ACE inhibitors – improve blood flow
- Statins – control cholesterol levels
3️⃣ Surgical Treatment
- Angioplasty: Blocked artery open kiya jata hai balloon aur stent se
- CABG (Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting): Blocked area ke around new route banaya jata hai blood flow ke liye
🩺 Nursing Management
| Aspect | Nursing Action |
|---|---|
| Assessment | Monitor vital signs, ECG, chest pain |
| Position | Semi-Fowler’s position to ease breathing |
| Oxygen | Administer as prescribed |
| Pain Relief | Give prescribed analgesics |
| Monitoring | Watch for arrhythmias, hypotension |
| Diet Care | Low-fat, low-salt diet |
| Education | Advise lifestyle modification, avoid stress |
| Emotional Support | Counsel patient & family members |
💪 Health Education for Patient
- Stop smoking and alcohol
- Maintain ideal body weight
- Eat healthy (low fat, high fiber diet)
- Exercise regularly (as advised by doctor)
- Control diabetes and BP
- Take medicines regularly
- Avoid stress and tension
- Regular follow-up with cardiologist